Surface Water Treatment Plant
Surface Water
Treatment Plant –
ASurface Water Treatment Plant (SWTP) i. To ensure a continuous supply
of safe and clean water, modern surface water treatment plants apply multiple
processes that eliminate impurities, bacteria, and harmful chemicals. These
plants play a crucial role in providing safe drinking water to households,
industries, municipalities, and commercial establishments.
In
today’s world, where water quality is threatened by urbanization, industrial
growth, and climate change, the role of surface water treatment plants has
become more significant than ever.
Importance of Surface Water Treatment
Surface
water is naturally prone to contamination due to its exposure to the
environment. Industrial discharge, agricultural runoff,
and sewage waste often mix with rivers and lakes, carrying harmful pollutants,
chemicals, and microorganisms. Drinking untreated surface water can lead to
serious health problems such as cholera, diarrhea, hepatitis, and typhoid.
A
surface water treatment plant provides an effective solution by:
- Removing suspended particles and sediments. Eliminating disease-causing bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Reducing chemical contaminants such as pest
- Improving taste, odor, and
color of water.
- Ensuring compliance with WHO
and local water quality standards.
By
purifying raw water into safe and potable water, these treatment plants
safeguard human health and support sustainable development.
Step-by-Step Process of Surface Water
Treatment
Surface
water treatment involves multiple carefully designed stages. Each stage focuses
on removing specific impurities to make water safe and reliable.
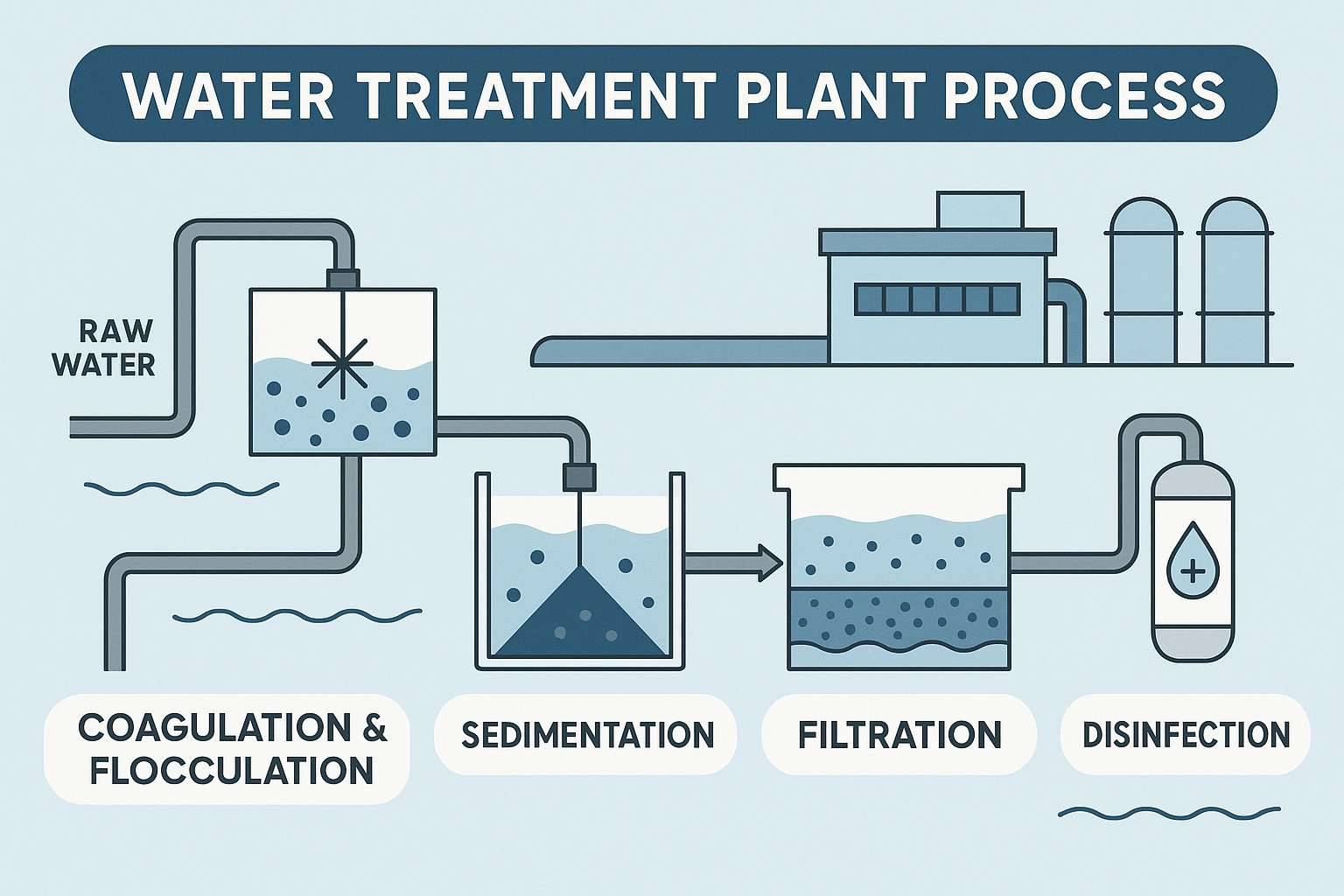
1. Intake and Screening
Water
is drawn from rivers, lakes, or reservoirs and passed through large screens to
remove leaves, branches, plastics, and other debris.
2. Coagulation and
Flocculation
Chemicals
such as alum or ferric chloride are added to destabilize fine particles. These
particles combine to form larger clusters called flocs, which are easier to
remove.
4. Filtration
The
clarified water passes through layers of sand, gravel, and activated carbon filters.
Filtration eliminates remaining particles, organic matter, and microorganisms.
5. Disinfection
To
kill harmful pathogens, disinfectants like chlorine, ozone, or ultraviolet (UV)
light are applied. This step ensures that the water remains safe during storage
and distribution.
6. pH Adjustment and Chemical
Balancing
The
treated water is chemically balanced by adjusting pH levels. Lime, soda ash, or
carbon dioxide may be added to stabilize acidity and alkalinity.
7. Storage and Distribution
Finally,
purified water is stored in clean reservoirs and supplied to households,
industries, and institutions through pipelines.
Advantages of a Surface Water
Treatment Plant
Investing
in a surface water treatment system offers numerous benefits:
- Safe Drinking Water Supply – Reduces health risks by
eliminating dangerous contaminants.
- Public Health Protection – Lowers cases of
waterborne diseases in communities.
- Cost-Effective Large-Scale Purification – Efficiently treats large volumes of water for municipal use. Environmental Sustainability – Prevents pollutants from spreading i
- Reliable Water Quality – Provides consistent and
controlled purification results.
- Industrial Applications – Ensures water quality
suitable for cooling, processing, and manufacturing.
- Enhanced Taste and Odor – Removes unpleasant smells
and flavors from raw water.
Applications of Surface Water
Treatment
Surface
water treatment plants are used in various sectors:
- Municipal Water Supply – Cities and towns rely on
SWTPs for safe tap water.
- Industrial Operations – Factories require purified water for production processes. Agriculture and Irrigation – Ensures clean wate
- Hospitals and Institutions – Provides safe water
essential for health facilities.
- Hotels and Commercial Spaces – Guarantees clean water
for guests and operations.
Modern Technologies in Surface Water
Treatment
With
growing water demand and pollution challenges, modern plants use advanced
methods to improve efficiency and sustainability:
- Membrane Filtration – Ultrafiltration and
nanofiltration membranes remove fine particles and microorganisms.
- Reverse Osmosis (RO) – Removes dissolved salts
and contaminants, ensuring superior purity.
- Automated Monitoring Systems – Ensure real-time water
quality control.
- Advanced Oxidation Processes
(AOPs) –
Break down harmful organic compounds.
- Energy-Efficient Designs – Reduce operational costs
and carbon footprint.
These
innovations make water treatment faster, more reliable, and environmentally
friendly.
:
- Surface water treatment
plant
- Surface water purification system Water filtration technology Drinking water treatment solutions Safe municipal water supply
- Industrial water
purification plant
- Advanced water treatment
process
- Sustainable clean water
solutions
- Surface water filtration
plant
- Water treatment for
industries
Challenges and Future of Surface
Water Treatment
While surface water treatment plants are highly effective, they face challenges such as rising pollution levels, aging infrastructure, and increasing operational costs. Climate change is also affecting the availability and quality of surface water sources. The future of surface water treatment lies in adopting sustainable te
change is also affecting the availability and quality of surface water sources.
The future of surface water treatment lies in adopting sustainable te
chnologies, renewable energy solutions, and smart monitoring systems.
Governments, industries, and communities must collaborate to ensure safe,
affordable, and accessible water for all.
Conclusion
A
surface water treatment plant is a cornerstone of modern water
management, turning polluted and unsafe water into clean, drinkable, and
high-quality water. Through processes like coagulation, filtration, and
disinfection, these plants protect communities from waterborne diseases,
support industrial growth, and safeguard the environment.
Investing
in a reliable surface water treatment plant means investing in public
health, environmental safety, and sustainable development.





